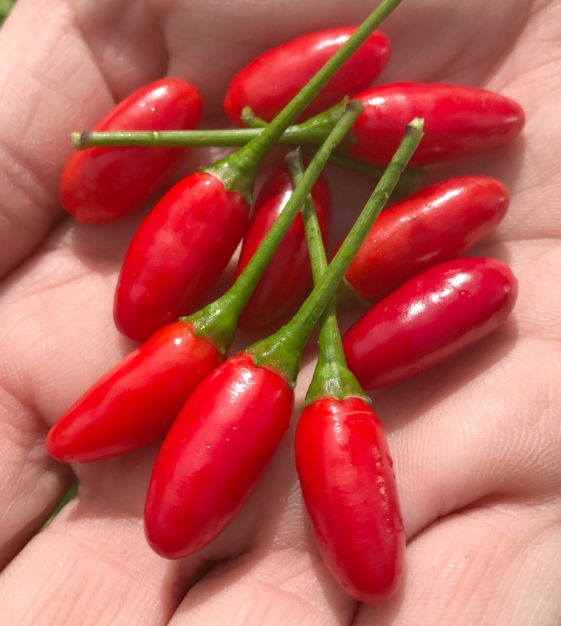
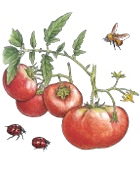
Tabasco Hot Chile Pepper
One packet of about 30 seeds
- Buy 10 for $4.75 each and save 10%
- Buy 50 for $3.95 each and save 25%
- Information
- Gardening Tips
 Best raised as transplants sown indoors 6 to 8 weeks prior to setting out after the last spring frost date, Hot Peppers love heat: afficionados theorize that the hotter the growing conditions, the hotter the Pepper. The heat in Peppers is related to the amount of capsaicin within the tissues and seeds. We include heat unit measurements (known as Scoville units) and arrange the Peppers in ascending incendiary order! At the height of harvest, hold a roast. Place picked Peppers on a hot grill, turning them until all sides are charred and blistered black. Pile them all in a paper bag so that they steam each other's skins off. Once they are cool enough to handle, peel off the skins, remove the stems and slice into long pieces, scraping away the seeds. Freeze in airtight plastic bags for use on sandwiches and in sauces, stews and casseroles through the winter. Deer resistant.
Best raised as transplants sown indoors 6 to 8 weeks prior to setting out after the last spring frost date, Hot Peppers love heat: afficionados theorize that the hotter the growing conditions, the hotter the Pepper. The heat in Peppers is related to the amount of capsaicin within the tissues and seeds. We include heat unit measurements (known as Scoville units) and arrange the Peppers in ascending incendiary order! At the height of harvest, hold a roast. Place picked Peppers on a hot grill, turning them until all sides are charred and blistered black. Pile them all in a paper bag so that they steam each other's skins off. Once they are cool enough to handle, peel off the skins, remove the stems and slice into long pieces, scraping away the seeds. Freeze in airtight plastic bags for use on sandwiches and in sauces, stews and casseroles through the winter. Deer resistant.
Average seed life: 2 years.
 Best raised as transplants sown indoors 6 to 8 weeks prior to setting out after the last spring frost date, Hot Peppers love heat: afficionados theorize that the hotter the growing conditions, the hotter the Pepper. The heat in Peppers is related to the amount of capsaicin within the tissues and seeds. We include heat unit measurements (known as Scoville units) and arrange the Peppers in ascending incendiary order! At the height of harvest, hold a roast. Place picked Peppers on a hot grill, turning them until all sides are charred and blistered black. Pile them all in a paper bag so that they steam each other's skins off. Once they are cool enough to handle, peel off the skins, remove the stems and slice into long pieces, scraping away the seeds. Freeze in airtight plastic bags for use on sandwiches and in sauces, stews and casseroles through the winter. Deer resistant.
Best raised as transplants sown indoors 6 to 8 weeks prior to setting out after the last spring frost date, Hot Peppers love heat: afficionados theorize that the hotter the growing conditions, the hotter the Pepper. The heat in Peppers is related to the amount of capsaicin within the tissues and seeds. We include heat unit measurements (known as Scoville units) and arrange the Peppers in ascending incendiary order! At the height of harvest, hold a roast. Place picked Peppers on a hot grill, turning them until all sides are charred and blistered black. Pile them all in a paper bag so that they steam each other's skins off. Once they are cool enough to handle, peel off the skins, remove the stems and slice into long pieces, scraping away the seeds. Freeze in airtight plastic bags for use on sandwiches and in sauces, stews and casseroles through the winter. Deer resistant.
Average seed life: 2 years.